WOMEN
HIGH COMPLEXITY
This involves extracting the oocytes from the woman's ovary by follicular puncture and then fertilizing them in the laboratory with the man's sperm (from the partner or a sperm bank).
Conventional technique. The oocytes and sperm are placed in the same culture dish and left to fertilize spontaneously.
Intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI). The sperm is injected directly into the oocyte using microinjection. Used in cases of moderate to severe male factor infertility.
This is particularly suitable for women who cannot have children with their own eggs. It is a variant of in vitro fertilization (IVF) in which the oocytes belong to an anonymous donor.

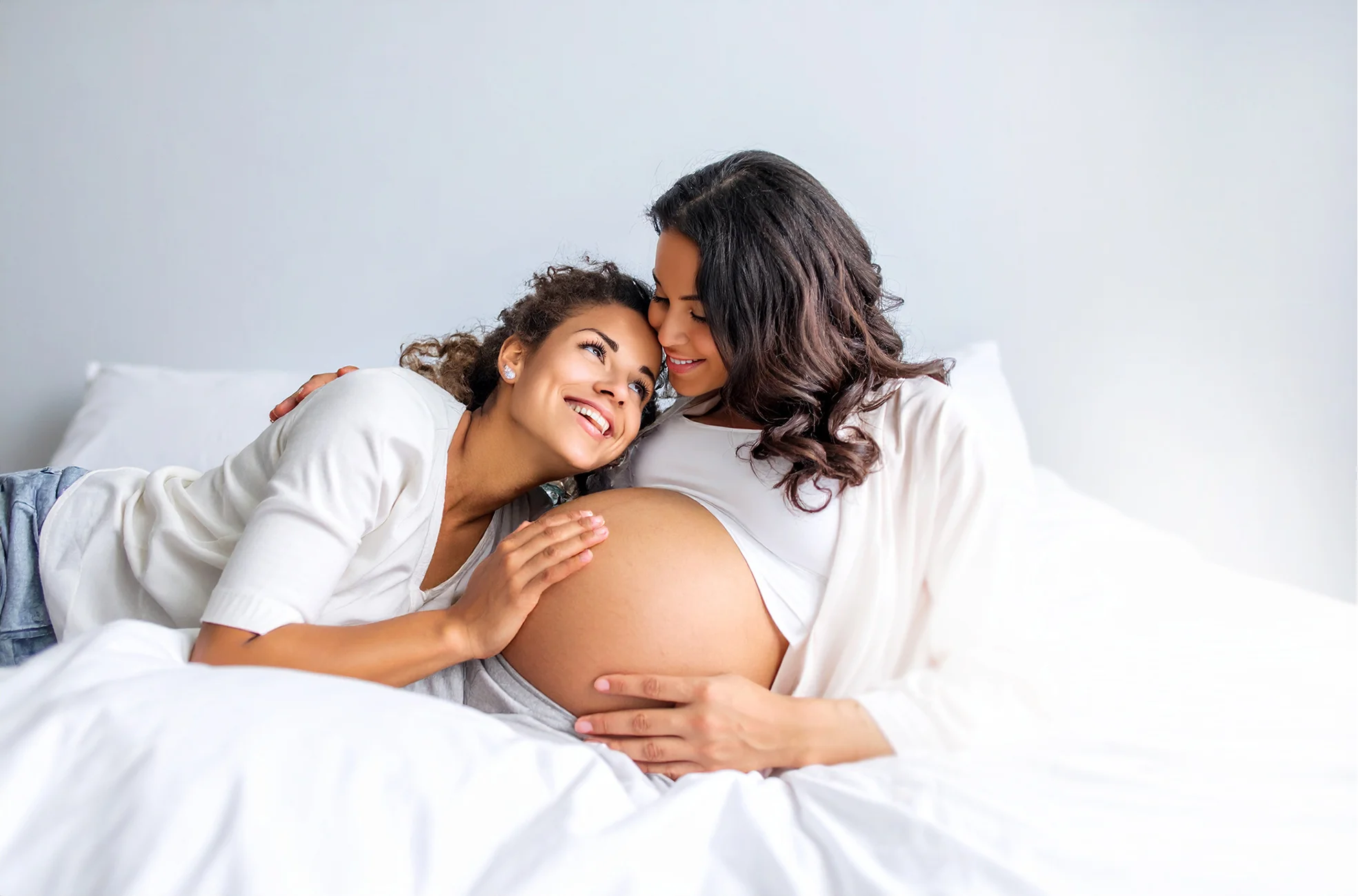
Treatment indicated for same-sex couples who decide to share motherhood. One member of the couple provides the oocytes while the other carries the pregnancy. The oocytes are extracted from the woman who provides them through a process of ovarian stimulation and subsequent ovarian puncture. The process is completed with in vitro fertilization using donor sperm.

Oocyte cryopreservation is a technique that allows women to preserve their fertility for the future. It consists of a procedure in which the oocytes are extracted, frozen, and stored for later use when the time comes.
The reasons for this may be social or due to medical circumstances that could affect reproductive capacity in the future.

LOW COMPLEXITY
Intrauterine insemination (IUI) is a low-complexity assisted reproduction technique in which sperm is introduced into the woman's uterus through a small cannula.
It can be performed with the partner's semen or with semen from a sperm bank.
It is a simple, outpatient procedure whose goal is to bring the gametes closer together to increase the chances of pregnancy.
MEN
TREATMENTS
Tissue is extracted from the testicles through minor surgery to determine the presence or absence of sperm. Laboratory work is then carried out to determine the quality of production and detect any possible pathologies.
The sperm is injected directly into the egg using microinjection. This technique is used in cases of moderate to severe male factor infertility.

TESTS
A test that measures the quantity, motility, and shape of sperm, as well as other biochemical parameters of semen, using the reference values established by the World Health Organization (WHO).
A test that measures the condition of sperm DNA, as in certain situations it can be fragmented or damaged, thus hindering pregnancy.
A method of separating motile sperm that allows those with the best motility to be selected and separated for subsequent use in low or high complexity techniques.
A method of separating sperm by centrifugation of the sample on gradients. Those with the highest motility are separated from the rest of the cells and seminal plasma by a difference in density. They can then be used for low or high complexity techniques.

A selection method in which spermatozoa are "filtered" from the sample using magnetic microspheres to separate those with low functional and reproductive quality, thus obtaining a sample with greater fertilization potential.